Chapter 15 Git Command Line Interface (CLI)
15.1 Git Command Workflow
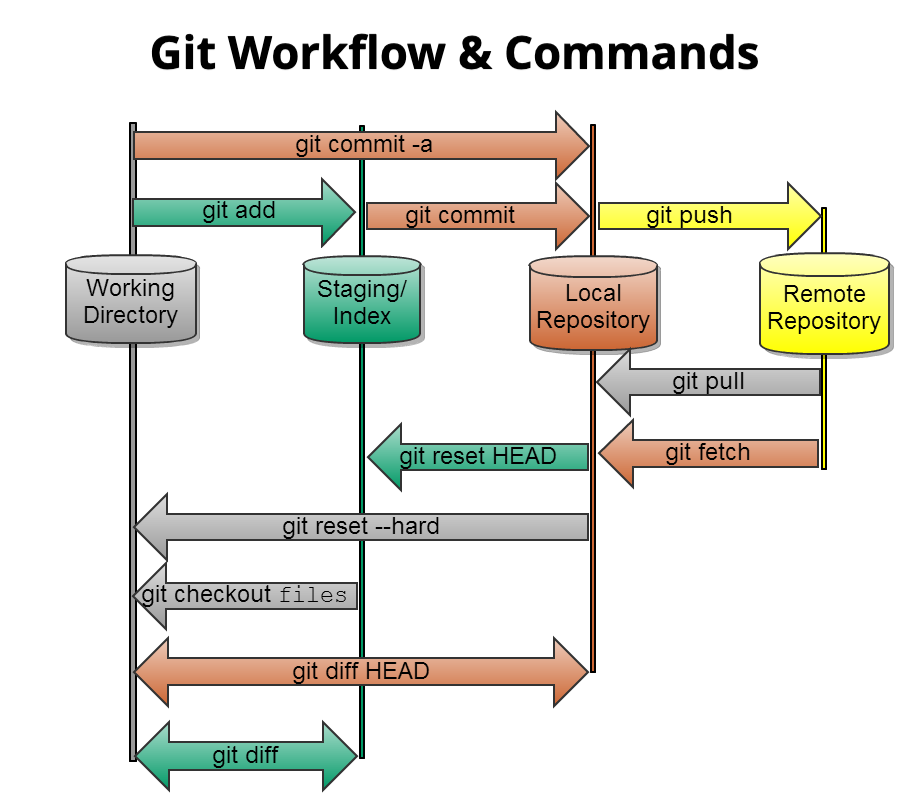
15.2 Git Commands
These are the primary commands for working with git from the commandline.
Important Note - We will use RStudio IDE to abstract away much of the git workflow. RStudio is integrated tightly with git and GitHub, which is a massive productivity booster.
15.2.1 General Commands
git --help- Use help to investigate the available commands.git --version- Useful for getting the version and checkinggitinstallation.
15.2.2 Local Repo Setup
No Remote Repo set up?
git init- Initialize a Local Repogit commit- Done to initialize (add) your files to the Local Repo.
Remote Repo already set up?
git clone- Clones a remote repo to your local machine. We do this to get software onto EC2 Servers.
15.2.3 GitHub Repo Setup
Important: Make sure a blank repo exists. Then:
git remote add origin https://github.com/user_name/repository.git- Used to link a local repository with agit push -u origin master- Pushes your initial commit on your Local Repo to the Remote Repo (e.g. GitHub).
15.2.4 Git Workflow
git commit- Adds snapshots of changed files to your Local Repo.git push- Pushes committed files from your Local Repo to your Remote Repo (e.g. GitHub)git pull- Pulls the remote repository files to your local repository
15.2.5 Branches
git status- Find the branch you are currently ongit branch- Creates a new branchgit checkoutswitches the Local Repository to the specified branchgit merge- Merges a branch with the master. This is typically done via “Pull Requests”.


Have a question? Leave a comment.