
Anomaly Detection
Matt Dancho
2025-08-29
Source:vignettes/TK08_Automatic_Anomaly_Detection.Rmd
TK08_Automatic_Anomaly_Detection.RmdAnomaly detection is an important part of time series analysis:
- Detecting anomalies can signify special events
- Cleaning anomalies can improve forecast error
This tutorial will cover:
Data
This tutorial will use the wikipedia_traffic_daily
dataset:
## Rows: 5,500
## Columns: 3
## $ Page <chr> "Death_of_Freddie_Gray_en.wikipedia.org_mobile-web_all-agents", …
## $ date <date> 2015-07-01, 2015-07-02, 2015-07-03, 2015-07-04, 2015-07-05, 201…
## $ value <dbl> 791, 704, 903, 732, 558, 504, 543, 1156, 1196, 701, 829, 838, 11…Visualization
Using the plot_time_series() function, we can
interactively detect anomalies at scale.
wikipedia_traffic_daily %>%
group_by(Page) %>%
plot_time_series(date, value, .facet_ncol = 2)Anomalize: breakdown, identify, and clean in 1 easy step
The anomalize() function is a feature rich tool for performing anomaly detection. Anomalize is group-aware, so we can use this as part of a normal pandas groupby chain. In one easy step:
- We breakdown (decompose) the time series
- Analyze it’s remainder (residuals) for spikes (anomalies)
- Clean the anomalies if desired
anomalize_tbl <- wikipedia_traffic_daily %>%
group_by(Page) %>%
anomalize(
.date_var = date,
.value = value,
.iqr_alpha = 0.05,
.max_anomalies = 0.20,
.message = FALSE
)
anomalize_tbl %>% glimpse()## Rows: 5,500
## Columns: 13
## Groups: Page [10]
## $ Page <chr> "Death_of_Freddie_Gray_en.wikipedia.org_mobile-web_a…
## $ date <date> 2015-07-01, 2015-07-02, 2015-07-03, 2015-07-04, 201…
## $ observed <dbl> 791, 704, 903, 732, 558, 504, 543, 1156, 1196, 701, …
## $ season <dbl> 9.2554027, 13.1448419, -20.5421912, -24.0966839, 0.4…
## $ trend <dbl> 748.1907, 744.3101, 740.4296, 736.5490, 732.6684, 72…
## $ remainder <dbl> 33.553930, -53.454953, 183.112637, 19.547687, -175.1…
## $ seasadj <dbl> 781.7446, 690.8552, 923.5422, 756.0967, 557.5091, 50…
## $ anomaly <chr> "No", "No", "No", "No", "No", "No", "No", "No", "No"…
## $ anomaly_direction <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0…
## $ anomaly_score <dbl> 83.50187, 170.51076, 66.05683, 97.50812, 292.21517, …
## $ recomposed_l1 <dbl> -328.3498, -328.3409, -365.9085, -373.3435, -352.636…
## $ recomposed_l2 <dbl> 2077.354, 2077.362, 2039.795, 2032.360, 2053.067, 20…
## $ observed_clean <dbl> 791.000, 704.000, 903.000, 732.000, 558.000, 504.000…The anomalize() function returns:
- The original grouping and datetime columns.
-
The seasonal decomposition:
observed,seasonal,seasadj,trend, andremainder. The objective is to remove trend and seasonality such that the remainder is stationary and representative of normal variation and anomalous variations. -
Anomaly identification and scoring:
anomaly,anomaly_score,anomaly_direction. These identify the anomaly decision (Yes/No), score the anomaly as a distance from the centerline, and label the direction (-1 (down), zero (not anomalous), +1 (up)). -
Recomposition:
recomposed_l1andrecomposed_l2. Think of these as the lower and upper bands. Any observed data that is below l1 or above l2 is anomalous. -
Cleaned data:
observed_clean. Cleaned data is automatically provided, which has the outliers replaced with data that is within the recomposed l1/l2 boundaries. With that said, you should always first seek to understand why data is being considered anomalous before simply removing outliers and using the cleaned data.
The most important aspect is that this data is ready to be visualized, inspected, and modifications can then be made to address any tweaks you would like to make.
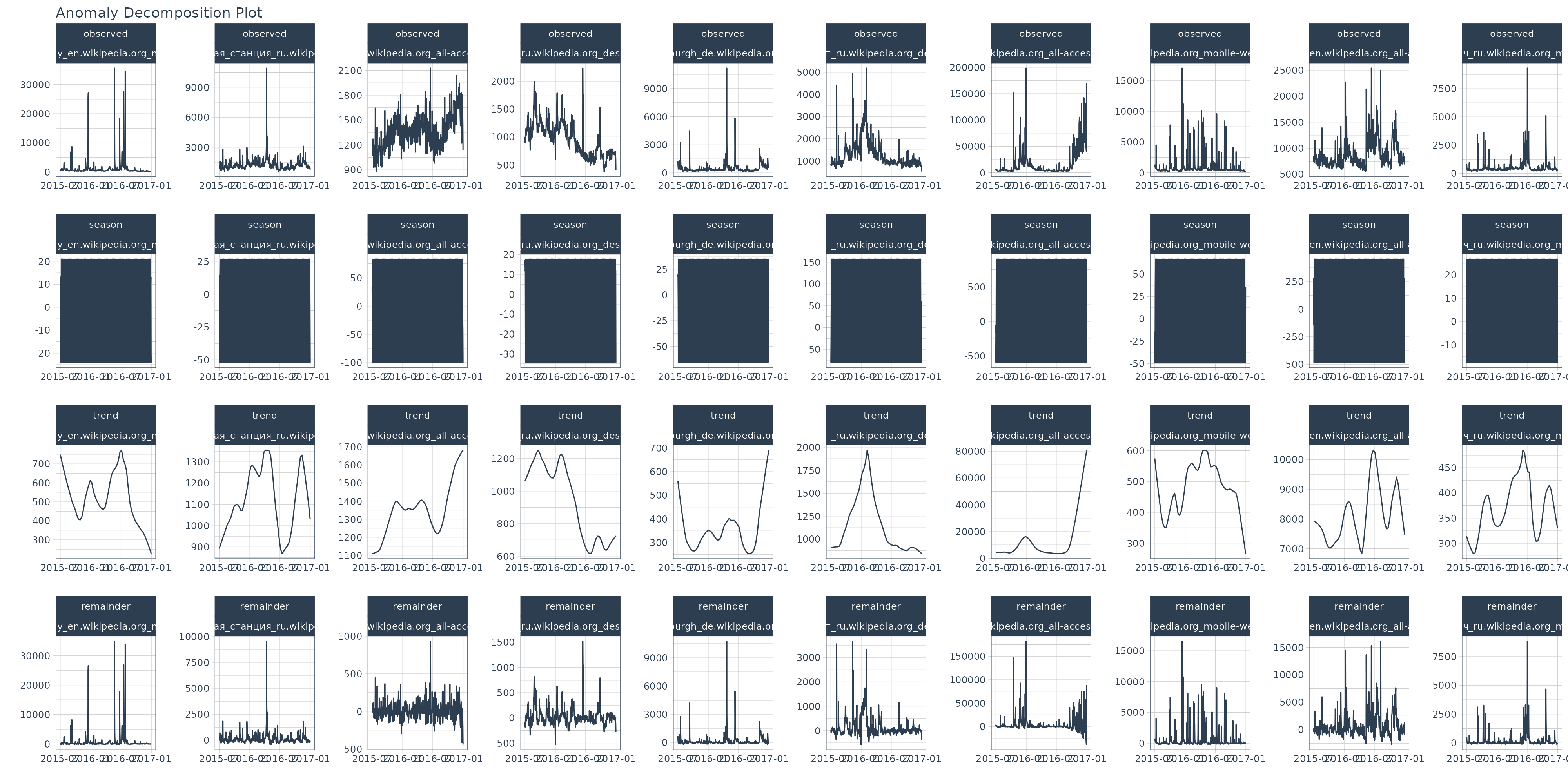
Anomaly Visualization 1: Seasonal Decomposition Plot
The first step in my normal process is to analyze the seasonal decomposition. I want to see what the remainders look like, and make sure that the trend and seasonality are being removed such that the remainder is centered around zero.
anomalize_tbl %>%
group_by(Page) %>%
plot_anomalies_decomp(
.date_var = date,
.interactive = FALSE
)
Anomaly Visualization 2: Anomaly Detection Plot
Once I’m satisfied with the remainders, my next step is to visualize the anomalies. Here I’m looking to see if I need to grow or shrink the remainder l1 and l2 bands, which classify anomalies.
anomalize_tbl %>%
group_by(Page) %>%
plot_anomalies(
date,
.facet_ncol = 2
)Anomaly Visualization 3: Anomalies Cleaned Plot
There are pros and cons to cleaning anomalies. I’ll leave that discussion for another time. But, should you be interested in seeing what your data looks like cleaned (with outliers removed), this plot will help you compare before and after.
anomalize_tbl %>%
group_by(Page) %>%
plot_anomalies_cleaned(
date,
.facet_ncol = 2
)Learning More
My Talk on High-Performance Time Series Forecasting
Time series is changing. Businesses now need 10,000+ time series forecasts every day. This is what I call a High-Performance Time Series Forecasting System (HPTSF) - Accurate, Robust, and Scalable Forecasting.
High-Performance Forecasting Systems will save companies MILLIONS of dollars. Imagine what will happen to your career if you can provide your organization a “High-Performance Time Series Forecasting System” (HPTSF System).
I teach how to build a HPTFS System in my High-Performance Time Series Forecasting Course. If interested in learning Scalable High-Performance Forecasting Strategies then take my course. You will learn:
- Time Series Machine Learning (cutting-edge) with
Modeltime- 30+ Models (Prophet, ARIMA, XGBoost, Random Forest, & many more) - NEW - Deep Learning with
GluonTS(Competition Winners) - Time Series Preprocessing, Noise Reduction, & Anomaly Detection
- Feature engineering using lagged variables & external regressors
- Hyperparameter Tuning
- Time series cross-validation
- Ensembling Multiple Machine Learning & Univariate Modeling Techniques (Competition Winner)
- Scalable Forecasting - Forecast 1000+ time series in parallel
- and more.